Early Signs of a Brain Tumour You Shouldn’t Ignore

Some symptoms seem ordinary—until they aren’t.
We all get headaches, fatigue, stress, dehydration—most of the time, there’s a simple explanation. But sometimes, the body sends quieter, more persistent messages. A change in how you speak. Blurred vision that lingers. A headache that returns day after day, stronger each time.
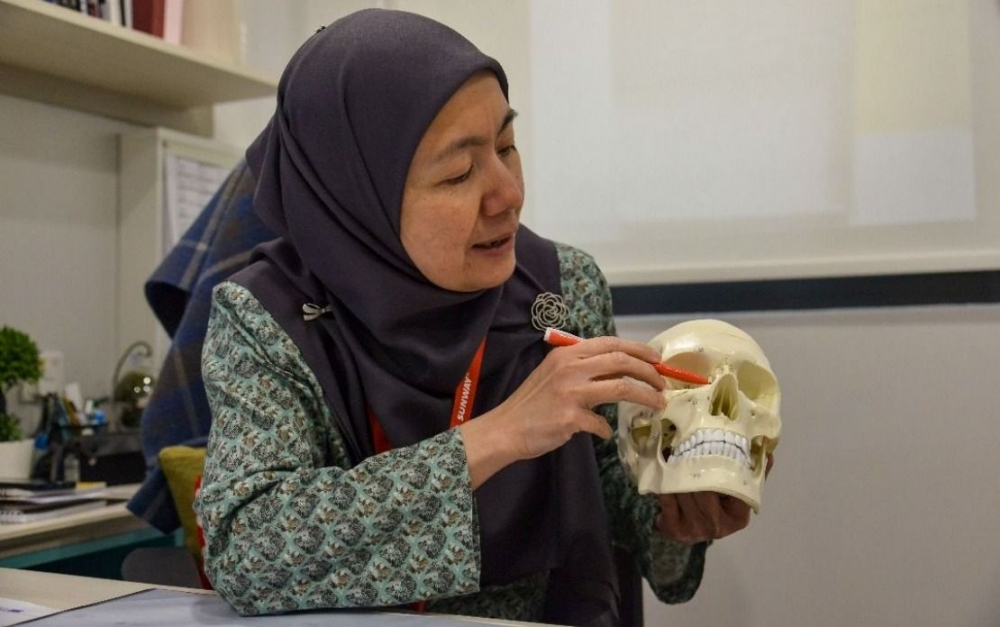
These subtle changes might not feel urgent at first. But in some cases, they are early signs of something deeper — such as a brain tumour. Let’s understand these warning signs more clearly with insights from Dr. Mah Jon Kooi, Consultant Neurosurgeon at Sunway Medical Centre Velocity.
What Is a Brain Tumour?
A brain tumour is a growth of abnormal cells in or around the brain. Some are slow-growing and noncancerous (benign). Others are malignant and can spread quickly. But even a benign tumour can compress on nearby brain tissue, affecting how we think, move, or feel.
Brain tumours can develop:
-
In the brain itself (primary tumours)
-
Or spread from cancer elsewhere in the body (secondary or metastatic tumours)
The impact depends not just on the location of the tumour, the staging or grading of the tumour, and tumour’s size.
Early Signs That Shouldn’t Be Overlooked
Symptoms often begin gradually, and they can easily be mistaken for more common issues. But when they persist or appear together, it’s important to take them seriously.
Watch for:
-
Frequent or worsening headaches, especially in the morning
-
Vision changes, such as double vision or partial loss of sight
-
Nausea or vomiting without an obvious cause
-
Difficulty with speech or memory
-
Weakness, numbness, or loss of balance
-
Personality changes or unusual behaviour
-
New-onset seizures
-
Hearing loss or ringing in one ear
Not every headache is cause for alarm. But when new symptoms appear, or old ones change in intensity and frequency, it’s worth checking in with a doctor.
Why Some Tumours Go Unnoticed
Some brain tumour arises from neuro silent area (non-eloquent) region of the brain, thus making the symptoms less obvious or subtle for the patient. This symptom might be missed until it grows to a significant size, compressing to the surrounding areas and giving noticeable symptoms.
The brain doesn’t always respond to change in obvious ways. A tumour pressing on a speech centre might affect your words. One near the optic nerve might blur your vision. But a tumour in a less active part of the brain might not cause noticeable symptoms—until it becomes large enough to affect surrounding areas.
That’s why awareness is key. Knowing the early signs can help lead to earlier diagnosis, when treatment is more effective and outcomes are better.
Who Is at Risk?
While brain tumours can occur at any age, certain factors may raise the risk:
-
Older age
-
Previous exposure to high-dose radiation
-
Inherited genetic conditions
-
A personal or family history of tumours
-
Cancer elsewhere in the body
What to Expect from Diagnosis and Treatment
If a brain tumour is suspected, your doctor may order imaging tests (MRI or CT scan) and neurological evaluations. Treatment options depend on the tumour’s type and location, and may include:
-
Surgery (open surgery, image-guided surgery and endoscopic)
-
Radiation therapy ( Conventional, Stereotactic)
-
Chemotherapy or targeted therapy
-
Active monitoring (watchful waiting approach)
When to Seek Help
Migraines are more than just head pain. They can mimic other conditions or go unnoticed entirely. By recognising the broader spectrum of migraine symptoms, you take an important step toward better brain health and overall wellbeing.
If you’re exploring options for neurology services in KL, can visit our neuroscience centre, where care is guided by experienced professionals and supported by advanced diagnostic tools.
If you’ve been experiencing unusual symptoms or persistent discomfort, speaking to a medical professional could help provide clarity and reassurance.
这篇文章对您有帮助吗?
有2 位用户在 2 位中觉得这很有帮助。
Suggest to Read









